Square
In geometry, a square is a regularquadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, or (100-gradian angles or right angles).[1] It can also be defined as a rectangle in which two adjacent sides have equal length. A square with vertices ABCD would be denoted ABCD.
Properties
A square is a special case of a rhombus (equal sides, opposite equal angles), a kite (two pairs of adjacent equal sides), a trapezoid (one pair of opposite sides parallel), a parallelogram (all opposite sides parallel), a quadrilateral or tetragon (four-sided polygon), and a rectangle (opposite sides equal, right-angles) and therefore has all the properties of all these shapes, namely:[5]
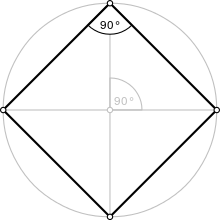
- The diagonals of a square bisect each other and meet at 90°
- The diagonals of a square bisect its angles.
- Opposite sides of a square are both parallel and equal in length.
- All four angles of a square are equal. (Each is 360°/4 = 90°, so every angle of a square is a right angle.)
- All four sides of a square are equal.
- The diagonals of a square are equal.
- The square is the n=2 case of the families of n-hypercubes and n-orthoplexes.
- A square has Schläfli symbol {4}. A truncated square, t{4}, is an octagon, {8}. An alternated square, h{4}, is a digon, {2}.
Perimeter and area
The perimeter of a square whose four sides have length  is
is
and the area A is



No comments:
Post a Comment